Rwanda's
Wholesale and Retail Trade sector stands as a pillar of economic activity,
employing a substantial portion of the nation's working-age population. This
article delves into the intricacies of the sector's workforce, offering
insights gleaned from the 2022 report by the Rwanda Development Board (RDB).
Join us as we explore key facets such as employment distribution, educational
backgrounds, gender dynamics, enterprise statuses, and the future outlook
within this vital sector.
Workforce
Composition: A Snapshot of Diversity
In
2022, the Wholesale and Retail Trade sector boasted a workforce of 372,408
individuals, with a balanced gender representation. The sector's youthfulness
is evident, with the average working age pegged at 36 years. This demographic
trend highlights the sector's appeal to the younger workforce.
Source: overview of the
wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles Sector-
2022 published by RDB.
Educational Attainment and Skill Diversity: Nurturing Talent Across Fields
Over 52.89% of the workforce has completed at most primary schools, showcasing the prevalence of elementary occupations. The sector acts as a magnet for individuals from diverse educational backgrounds, including social sciences, engineering, manufacturing, construction, humanities, and arts. A noteworthy aspect is the inclusivity of opportunities for those with middle to high levels of skills, with half of the jobs requiring at least lower secondary school, secondary school, or university-level education.
Source: overview of the
wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles Sector-
2022 education statistics published by RDB.
Occupational Diversity: A Kaleidoscope of Roles
Service and sales workers hold the lion's share, constituting 80.75% of the workforce. Craft and related trade workers, along with elementary occupations, collectively make up less than 10% of the sector's employment landscape.
Source: overview of the wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles Sector- 2022 employment statistics published by RDB.
Employment Trends: A Glimpse into the Past Five Years
The sector has witnessed a commendable 32% growth in total employment. However, gender disparities have emerged, with female employment decreasing by 10% and male employment experiencing a 33% decline.
Source: overview of the wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles Sector- 2022 employment statistics published by RDB.
Enterprise Analysis (2020): Unveiling the Business Landscape
Nearly 98% of enterprises within the sector are operational, underscoring its vitality. Male-dominated management structures prevail, with two-thirds of establishments led by male managers. The private sector is the undisputed leader, commanding 99.38% of the sector's establishments.
Source:
overview of the wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and
motorcycles Sector- 2022 employment statistics published by NISR
Enterprise Characteristics: The Building Blocks of Business
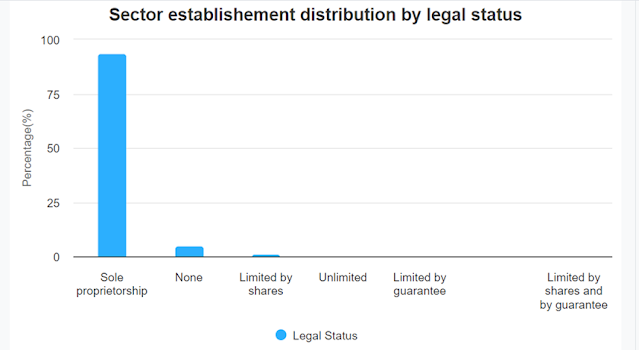
Sole proprietorships dominate the landscape, constituting 93.57% of enterprises. Local ownership is a prevailing theme, with 98.60% of establishments owned by Rwandans.
Source:
overview of the wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and
motorcycles Sector- 2022 legal status statistics published by RDB
Employment Status and Job Security: A Balancing Act
Approximately three-quarters of employed individuals operate as own-account workers without regular employees, highlighting job vulnerability. Job security remains a challenge, given the prevalence of self-employment without regular employees.
Source: overview of the wholesale and retail trade; repair of motor vehicles and motorcycles Sector- 2022 sector establishment formal/informal published by NISR
Rwanda's Wholesale and Retail Trade sector is a dynamic force, contributing
significantly to economic growth. While positive employment trends are evident,
addressing gender imbalances, fostering skill development, and enhancing job
security are imperative for sustained progress.
References:
- Rwanda
Development Board. "Wholesale and Retail Trade Sector- 2022 Workforce
Share Analytic Report."
- National
Institute of Statistics of Rwanda (NISR).
- Institute
of Economic and Business Studies (IEBS). "Annual State of Skills
Report."
Note:
The information presented is based on the data available as of the publication
date, and any subsequent developments may not be reflected in this article.







Comments
Post a Comment